the essentials in brief
- A raised bed should be about 90cm high
- You can easily build the balcony raised bed yourself from an old table, wooden boxes or a shelf
- The correct crop rotation must also be observed on the balcony
- Mulching protects the soil from drying out and from weeds
Instructions for building
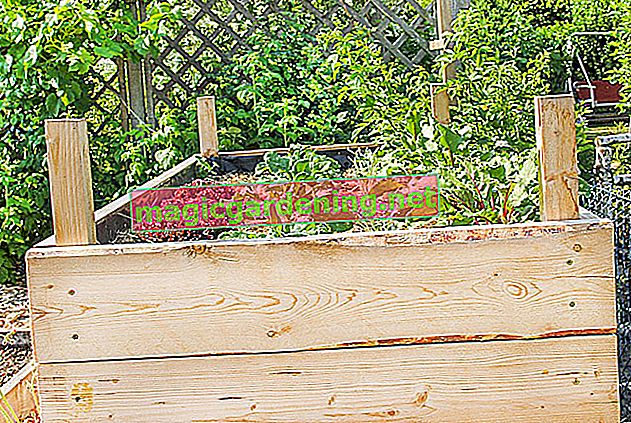
The construction of a raised bed for a balcony differs from constructions for the garden by supporting legs. They raise the bed and ensure that the plants are not shaded by balcony railings. For better mobility, you can equip the feet with rollers.
also read
- Building a covered fireplace - ideas and tips
- Trend upcycling: Build a great raised bed at low cost
- The best tips for raised beds
Wooden box on trestles
Cedar plant boxes are ideal as a raised bed. The wood is visually appealing and contains natural cedar oil, which protects against rot, mold and harmful insects. It's also light and sustainable. Choose boxes that are 30 centimeters deep. You can simply attach such planters to two wooden trestles to get a comfortable working height.
Converting an old table
If you have an old desk with a table top resting on a high frame, you can convert it into a raised bed. To ensure that lacquered or treated wood does not release toxic substances into the plant substrate, you should cover the plant box with harmless foil for safety.
What you need:
- Tape measure, hammer, drill, wire cutter and jigsaw (€ 43.99 on Amazon *)
- short nails, close-meshed wire, drainage fleece
- possibly foil to lay out
- thin slats made of cedar wood (about four inches wide and one inch thick)
Disused table that is suitable for planting
building instructions
Remove the table top so that only the wooden frame including the feet remains. Turn the table over and cut the wire mesh to the dimensions of the wooden frame. The wire is attached to the table from below with small nails.
Cut the slats so that they can be placed over the wire mesh as a frame and attached to the table. For better stability, cross battens are placed over the entire surface. Alternatively, you can cover the entire floor with battens. Turn the table over and cut the drainage fleece to the size of the planter.
Shelf with mini raised beds

If you already have an old bookshelf at hand that is suitable for outdoor use, you can convert it into a vertical raised bed with just a few resources. The shelves are provided with all-round side boards, so that a low plant box is created on each level. Alternatively, you can build a suitable shelf out of Euro pallets and provide this with intermediate shelves.
Many disused pieces of furniture can be converted into a raised bed with a little creativity and manual skill.
Small raised bed with cover
For each raised bed, you can build a cover yourself and convert the construction into a cold frame. To do this, you need old wooden planks, which you saw into two wedges. These wedges are mounted on the two shorter sides of the planter and serve as spacers for the roof.
A wooden board is attached to the long rear side of the raised bed so that the sloping roof structure is closed to the rear. Place a double-walled sheet on the slope that has been created. This can easily be cut to size with a craft knife.
How to assemble the roof:
- Place the cut double-walled sheet between two frames made of wooden planks
- connect both frames with nails or screws
- Attach the hinges to the inner frame
- Attach the hinges to the back of the roof support
material
The material used determines the longevity of the raised bed. Since weight plays a decisive role on the balcony, you should prefer light materials.
plastic
These variants are particularly light and easy to clean. They are weatherproof and inexpensive to buy. The construction is easy and requires no tools. Many models have a look that is reminiscent of terracotta or wood. There are also space-saving and simple designs that can be covered with a thermal hood. This means that plastic raised beds can be used for growing.
However, plastic models have ecological disadvantages compared to natural building materials, because recycling is difficult. The plastic should be colourfast so that there are no health risks.
metal
Such designs have a long service life and an unusual design. Metal raised beds are reminiscent of futuristic scenarios. They require less maintenance than wooden models. Depending on the material used, rust protection is recommended. Metal conducts heat better than wood. This brings advantages for cultivation and dangers for mature plants. In summer, you need to pay attention to optimal water supply and ventilation.
- Stainless steel : rustproof, robust and aesthetic
- Corten steel : forms rust, which protects the material from further corrosion.
- Aluminum : light, often with a zinc-aluminum coating
Wood

The natural raw material is renewable and does not pose any health risks as long as the wood is used untreated. It radiates naturalness and provides a rustic character. A raised bed made of solid wood is heavy, which is why only thin wood models are suitable for the balcony. They are easier to move. In general, softwoods are more suitable for balconies than hardwoods because of their light weight.
Soft wood is more susceptible to moisture and will weather faster without appropriate protection. Despite all protective measures, wood has the lowest longevity because it is susceptible to pests. You can also build a raised bed from old pallets, provided the wood does not contain any toxic substances.
| Price category | Properties and special features | |
|---|---|---|
| jaw | Cheap | prone to moisture |
| Spruce | Cheap | light, rots quickly |
| larch | expensive | very weatherproof and durable |
| Douglas fir | expensive | Avoid contact with the ground |
| Oak | expensive | difficult, very stable |
Other materials
Bed constructions can be built from different materials yourself. If the load-bearing capacity of the balcony allows, you can use discarded concrete slabs, lawn paving stones or gabions. If you have to cover the raised bed with foil, you should avoid PVC. The material often contains poisonous plasticizers that can be absorbed by the plants. EPDM foils made from natural rubber are more suitable.
What to look for in a DIY raised bed?
The raised bed on the balcony is an enclosed living space that must be well prepared. Such constructions are used for several years without the earth being replaced. It is therefore important that you take appropriate precautions and properly estimate the size.
size

In the trade, raised beds are offered in standard sizes, with the dimensions varying between 70 and 140 centimeters in width and between 70 and 90 centimeters high. A height of 90 centimeters is roughly equivalent to hip height. Such models ensure a back-friendly working posture. The width of the bed construction should not exceed the length of your arm so that you can work comfortably and effortlessly. You are relatively flexible in terms of length. You can adapt this to the space available on your balcony.
How deep should the plant liner be?
The depth of the plant liner should be between 30 and 50 centimeters. Shallow-rooted varieties develop their roots down to a depth of 20 centimeters. Since their roots grow in the upper layers of the soil, these plants need more frequent watering. Central roots need a depth of 50 centimeters.
- Flat-rooted: lettuce, onion, radish, spinach, celery, radishes
- Middle roots: carrots, beans, kohlrabi, peas, peppers, cucumber
Ideas and design options
Raised beds with their own floor are suitable for the balcony. Such models can be designed flexibly. Raised beds on castors can be easily repositioned and offer storage space on the floor. A narrow raised bed that stands directly on the ground can be clad with wooden planks. Small gaps between the boards provide space for rakes and hanging pots.
drainage
Raised table beds have limited space for filling, which is why a space-consuming drainage made of stones is less than optimal. In deeper constructions you can cover the floor with expanded clay (€ 17.50 at Amazon *). The beads absorb excess water and release it back to the substrate when necessary. If you equip the model with a water drain in the form of small holes on the floor, rainwater can easily drain away. To avoid unsightly stains on the balcony, you should put a tub under it.
Geotextile
Raised beds without drainage holes can be laid out with a special garden fleece made of geotextile (€ 84.99 on Amazon *). The dense fiber structure stores the water and releases it slowly. If the substrate is too moist, the water can slowly diffuse through the wooden floor and evaporate on the outside.
Tips on buying
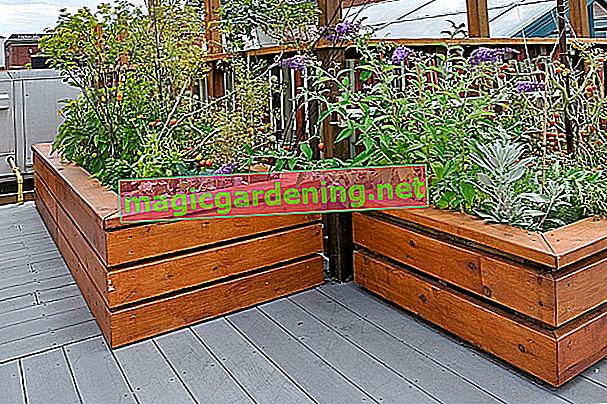

The range of raised beds for the balcony is large. Obi, Bauhaus, Dehner and Hornbach as well as Amazon and Ikea offer different models. There are inexpensive raised beds at the start of the season from Aldi and Tchibo. If you are new to this type of gardening, you can find out about used products on Ebay and test the possibilities.
Product selection:
- Jewel: balcony and terrace raised beds made from recycled plastic
- Kubi: designer raised bed made of stainless steel with vertical plants
- Jumbo: raised beds made of wood, metal or plastic with plug-in systems
- Landi: mobile raised beds and plant tables
What should I watch out for?
A good raised bed should be stable and have a little distance to the ground so that cold and frost cannot penetrate from the ground into the plant container. Size and material play an important role and determine the price. If you also want to use the raised bed as a cold frame, you should compare models with a special attachment.
Since the substrate should be completely replaced after a few years, the model design is an important decision point. Plastic tubs can be cleaned easily. Raised beds made up of a plug-in system are also practical. With these models, individual elements can be removed, which facilitates the exchange of earth.
Fill and plant
In order to exploit the maximum potential of a raised bed, you should fill it correctly. Which soil you use is just as important as the choice of plants. If the raised bed has different soil layers, a natural habitat is automatically created.
Digression
Why it is warmer in the raised bed
The temperature in a raised bed is up to eight degrees higher than in a flat bed. However, the natural decomposition processes only cause a drastic rise in temperature in the substrate for a short time. As soon as the material settles and the air is used up, no new oxygen comes in. Numerous microorganisms can no longer work in the soil under anaerobic conditions and slowly die off. However, a raised bed heats up faster from the outside in spring, as the large outer walls conduct the warmth of the sun's rays inside.Conventional layering
In a 50 centimeter high raised bed, the ground is covered with remains of wood and shrub cuttings. The first layer is about four inches high and is covered with a two-inch layer of grass clippings. Then fill a ten centimeter thick layer with biodegradable green waste that has not yet rotted. Another 25 centimeter thick layer of ripe compost provides the plants with enough nutrients to grow. In higher raised beds you can adjust the layer thickness accordingly.
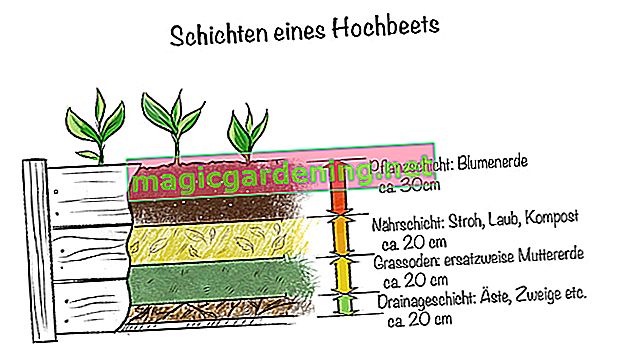
Experimental layering
There are different ways to fill the raised bed. If you ensure an adequate supply of nutrients, the stratification plays a subordinate role. You can also experiment and cover the bottom of the raised bed with bark mulch. The plant liner is filled with structurally stable soil, which has been loosened with lava chippings, coarse-grained sand or gravel. Also, mix some compost into the soil to meet the plants' nutritional needs.
What the filling has to do:
- high water holding capacity
- low settling and compaction of the material
- functioning habitat for microorganisms
planting
It is important that you plant the raised bed properly. In this way, you use the resources fully and achieve high yields over several years. The filled raised bed is very rich in nutrients and should be stocked with heavily consuming plants in the first few years. Central eaters are planted in the following years. Weak eaters still thrive in the raised bed in the later years. A mixed culture is also ideal so that the plants are not attacked by pests.
| group | Main plant | Good neighbors | |
|---|---|---|---|
| first and second year | Heavy Eater | cauliflower | Cucumber, beetroot, celery |
| third to fourth year | Central Eater | Carrots | Tomatoes, lettuce, onions |
| fifth to seventh year | Weak eaters | Peas | Herbs like dill, fennel, radishes |

Take advantage of heat generation
You can also plant the raised bed according to the natural heat development, so that you benefit from high yields throughout the gardening season. The bed becomes fuller as the year progresses, so you can harvest fresh vegetables or fruit throughout the season.
Planting plan by months:
- March to April: Spring plants such as arugula, parsley and radish
- End of April: add spring onions, leeks and onions
- from May: plant out preferred vegetables such as tomatoes, paprika and peppers
- in August: autumn salads, kale, endive
- September to October: Plant frost-resistant vegetables such as rocket, sprout broccoli or celery
Tips
If you've harvested everything before winter, you can bring fresh nutrients into the soil through horn shavings.
Maintain a raised bed
Raised beds must be sufficiently watered, especially in summer, so that the substrate does not dry out. You can do without additional fertilizers, because annual compost and mulch add nutrients to the substrate.
Fill up the substrate
Over the years the substrate settles because the microorganisms consume the organic components and convert them into soil. You should therefore refill the raised bed with fresh compost as soon as the soil level has dropped. The entire substrate should be renewed after six to seven years.
Tips
The used soil is ideal for the garden. Spread the substrate on vegetable and flower beds.
Mulching
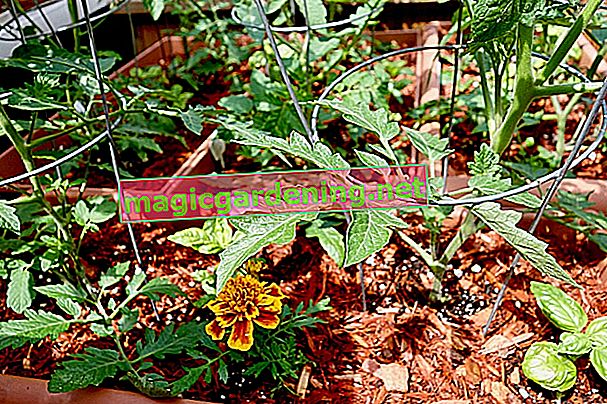

This measure is particularly important in raised beds, as the substrate dries out faster than in flat beds. In addition, the covering ensures that no unwanted herbs grow. Applied shortly before winter, the material protects the soil in the frosty season. In spring, the plants benefit from additional nutrients. Lawn cuttings, wood fibers or small-cut plants such as nettles or comfrey are suitable as a mulch layer.
Dig up
Raised beds are not dug up so that the layers do not get mixed up. In this way, a cosmos of its own can develop in which natural processes take place undisturbed. Before you plant the bed again in the following years, the top soil layer should be slightly loosened.
frequently asked Questions
When should I create my raised bed?
The ideal time is spring, as you can plant the raised bed with plants immediately after it has been filled. In autumn, a lot of material is produced by wood and lawn cutting measures, which can be filled into the raised bed. You can also let this grow over the course of a year and fill it up whenever biodegradable material is available.
Why is the substrate in the raised bed warmer?
In the first weeks after filling, microorganisms work and break down the biological material. After about four weeks, the temperature drops rapidly. Then the oxygen is used up and the microorganisms can no longer live under anaerobic conditions. The fact that a raised bed inside is still warmer than the substrate in the flat bed is due to the external warming. The sun shines on the walls, which means that the substrate warms up faster.
Which plants are suitable for the raised bed?
Basically, both flowering plants and herbs as well as vegetables and fruit bushes are suitable for cultivation in raised beds. The choice of plants is limited by the climatic conditions in their region. You should also equip the plant liner with plants whose root length does not extend to the ground.
How important is the layering in the raised bed?
In the raised bed, different materials are layered on top of each other, as it is difficult to regulate the water balance and the plants should benefit from the nutrients in the decomposable organic waste. A temperature increase due to decomposition processes only occurs in the first few weeks. Therefore the conventional stratification does not necessarily have to be retained.








