the essentials in brief
- There are numerous phosphate fertilizers with varying levels of phosphate between 5 and 52 percent.
- They should only be used if there is a proven lack of phosphate in the soil or plants.
- Phosphate fertilizers contain heavy metals such as cadmium and chromium, which are deposited in plants and animals as well as in the soil and groundwater.
- A soil analysis must be carried out before use, and the dosage can be reduced by adding manure.
What is phosphate fertilizer?
Phosphorus (P) together with nitrogen (N) and potassium (K) form the three main nutrients which are essential for the growth of plants and which are therefore the most important components in every full and NPK fertilizer. Sometimes there can be a lack of phosphorus, which significantly impairs the formation of flowers and fruit as well as the healthy growth of ornamental and useful plants. In this case, a special phosphorus fertilizer can help.
also read
- Lady's mantle - effect, application and use
- Nettle fertilizer: effect, production, use
- Complete fertilizers: types, composition and correct application
Phosphate fertilizers consist of the salts of phosphoric acid (H3PO4). Since pure phosphorus is only poorly soluble in water, it must first be chemically processed before it can be used as a fertilizer. Various acids break down the calcium phosphate required. Only then are the nutrients available to plants.
Composition and properties
"Globally, more uranium is mined in phosphate than is used in nuclear reactors."

The raw phosphorus required for phosphorus fertilizer is mostly obtained through mining from natural deposits that have formed from deposits of former marine animals that are millions of years old. Many of these deposits are located in the countries of North Africa as well as South Africa, Jordan, China and Russia. The world's largest phosphate producer is Saudi Arabia. In addition, rock phosphate is extracted from the remains of sea birds, known as guano. (€ 10.44 at Amazon *)
The plants take up the processed phosphorus through their roots, whereby the fertilizer is best available at a pH value between 6 and 7. Various phosphorus foliar fertilizers are available in stores, but these only help for a short time - the lion's share of the nutrient is ultimately absorbed by the roots.
Digression
Thomas flour - a cheap but problematic phosphate fertilizer
So-called Thomas flour is a very inexpensive phosphate fertilizer, which, however, should not be used due to its high proportion of the heavy metal chromium - the heavy metal is deposited in the soil and in the plants and also gets into the groundwater. Thomas flour is a waste product from iron ore smelting and is therefore highly polluted.Effects and effects
Phosphorus is an important component of every plant cell. The element is essential for the functioning of the metabolism in all ornamental and useful plants. A phosphorus deficiency, which is detected either by means of a growth depression in plants or, more often, by a soil analysis, should therefore be remedied immediately. The use of a phosphorus fertilizer has the following effects if it is applied correctly:
- Roots grow deeper, so the plants can be better supplied
- the bud and flower formation is supported
- Support of cell division and thus leaf and shoot growth
- Support of resistance to diseases and pests
So that the phosphorus fertilizer can work optimally, you should before its use
- conduct a soil analysis
- and only apply the phosphorus fertilizer if the analysis shows a deficiency
- then carry out a pH test
If the soil is too acidic (pH value below 5.5), it must first be brought into the optimal range between 6 and 6.5 by means of liming. If the result is more than 7, it is better to choose a water-soluble phosphate fertilizer.
But be careful: Phosphate fertilization not only affects the plants, but also directly affects the soil and the groundwater. Too high a proportion of phosphate in water can be recognized by excessive algae growth, and aquatic plants and aquatic organisms such as fish, snails, mussels and crabs die off due to the lack of oxygen. This effect can often be observed in bodies of water that are located in heavily farmed regions. This is why phosphate fertilization should only be carried out if it is really unavoidable.
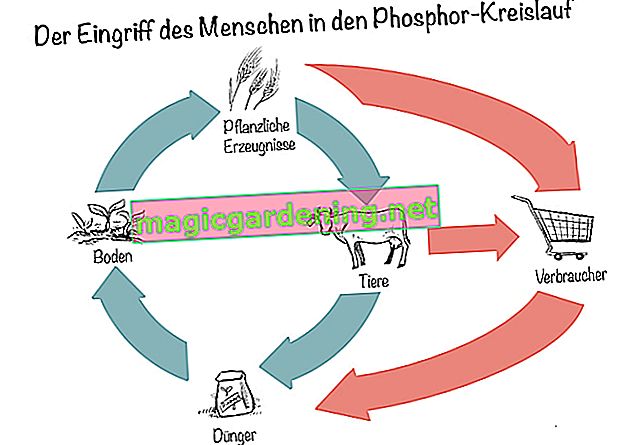
Digression
Caution, highly toxic!
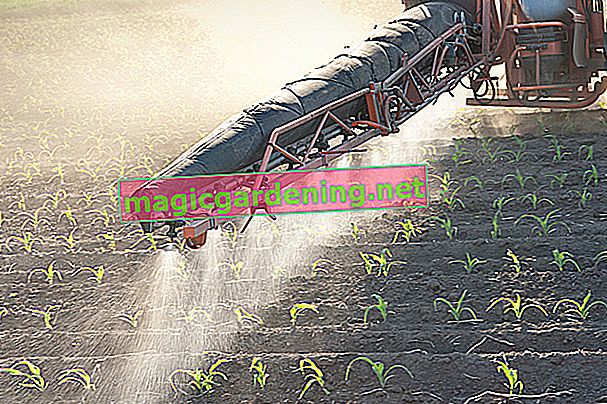

Phosphate fertilizers are indispensable, especially in industrial agriculture, in order to achieve the highest possible yields. However, these fertilizers are also very problematic as they are heavily contaminated with toxic heavy metals, especially uranium and cadmium. By using such a fertilizer, these toxins inevitably get into our food through plants and animals. There is currently no legal maximum uranium content in Germany, just a recommendation from the Federal Ministry of Food and Agriculture. Here the maximum value is 50 milligrams of uranium per kilogram of phosphate fertilizer.
Types of phosphate fertilizers
Numerous phosphorus fertilizers are available on the market especially for home and hobby gardens. In addition to pure phosphorus fertilizers, you can also choose complex fertilizers with a high phosphorus content. Typical examples are universal or complete fertilizers as well as NPK fertilizers, because in these products the three main nutrients nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium form the most important and thus the largest components in terms of quantity.
The following table provides you with an overview of common single and multi-component fertilizers.
| Type of fertilizer | Phosphate content | Special properties | price |
|---|---|---|---|
| Superphosphate | 18 percent | water-soluble granules, with NPK | approx. EUR 1.10 per kilogram |
| Superphosphate with sulfur | 18 percent | water-soluble granulate, also contains sulfur | approx. EUR 3.40 per kilogram |
| Phosphate potash / Thomas potash | 8 percent | Potash fertilizer with a high phosphorus content as well as magnesium and other trace elements | approx. EUR 2.10 per kilogram |
| Extensive phosphate potash fertilizer with long-term effects | 15 percent | PK fertilizer with magnesium and sulfur | approx. EUR 1.30 per kilogram |
| P 20 liquid phosphate fertilizer | 20 percent | Concentrate, to be diluted with water, also suitable for foliar fertilization | approx. 4 EUR per 100 millilter |
| Phosphor Plus liquid fertilizer | 7 percent | Additional fertilizer with phosphorus and potassium for flowering plants | approx. EUR 13.50 per liter |
| Thomaskali | 8 percent | granulated PK fertilizer with magnesium | approx. 0.90 cents per kilogram |
For the home and hobby garden, multi-component fertilizers that contain both phosphorus and other nutrients are usually completely sufficient. Phosphate fertilizers with a very high phosphate content, for example
- Diammon phosphate (DAP) with 46 percent phosphate content
- Monoammon phosphate (MAP) with 52 percent phosphate content
however, are primarily used in agriculture. Anyone who needs a fertilizer with a high phosphate content for the home garden is better off choosing so-called superphosphate. This contains calcium phosphate and sulfuric acid, with the phosphate content fluctuating between 16 and 22 percent depending on the manufacturer.
Correct application
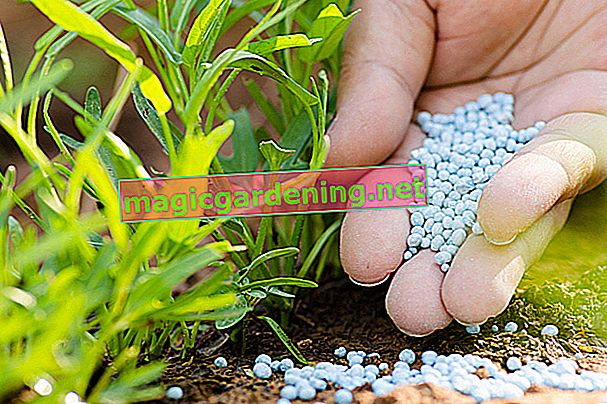

Phosphate fertilizers require appropriate handling in order to avoid possible overdosing and thus unnecessary exposure to heavy metals. It is not only a question of the correct, needs-based dosage, but also the timing and type of application.
time
When you carry out phosphate fertilization depends primarily on the specific product that you want to apply:
- Water-soluble phosphate fertilizers : such as B. Superphosphate comes as a basic fertilizer on the earth in spring. Choose granulated fertilizers as they will be released faster.
- Phosphate fertilizers with a high proportion of rock phosphates : are applied in autumn. They are particularly suitable for acidic soils / soils with a low pH value
Liquid fertilizers containing phosphates are practical, as you simply add them to the irrigation water and water the plants directly with it. You can also use these during the growing season.
Dosage and effects
video: Youtube
Phosphate fertilizers should be applied as close as possible to the roots, as this is the only place where they develop their effect. In contrast to nitrogen fertilization, you do not have to worry about root damage. And so is fertilized:
- Please note the manufacturer's instructions regarding dosage and use.
- The dosage also depends on the specific phosphate content of your garden soil.
- We recommend around 30 to 60 milligrams of phosphate fertilizer per square meter for superphosphate.
- Sprinkle the phosphate fertilizer directly on the root disc of the plant to be fertilized.
- Use a spreader to evenly fertilize larger areas, such as lawns.
- Work in the granules on the surface.
- Water vigorously so that the fertilizer dissolves and seeps into the soil.
Lower the dosage by applying organic fertilizer in the form of compost or manure at the same time. Manure, in particular, allows the amount of fertilizer to be reduced by up to 40 milligrams per square meter. When using compost, you need 15 milligrams less phosphate fertilizer per square meter.
frequently asked Questions
Are there alternatives to phosphate fertilizers?

Yes, fertilize your garden with manure. This contains a high proportion of natural phosphate (similar to sea bird droppings), but it takes some getting used to for some gardeners. Make sure that poultry manure, in particular, must have rotted well before you spread it! Otherwise, agronomists all over the world are researching alternatives to mineral phosphorus fertilizers - it is high time that the worldwide phosphorus deposits are gradually coming to an end.
Do you even need special phosphorus fertilizers in the garden?
No, with the exception of a deficiency confirmed by a soil sample, the use of phosphorus fertilizers in home and hobby gardens is practically superfluous, especially if the garden is mainly fertilized with manure and compost. Many supposed signs of a phosphorus deficiency in plants can also be traced back to other causes, which is why you should avoid fertilizing if possible, if only because of the high proportion of pollutants.
How do I perform a soil analysis?
Since a suspected lack of phosphorus should not be fertilized on suspicion, a soil analysis must be carried out beforehand. Of course, you don't do this yourself. You take soil samples from different places in your garden and send them to a specialized institute for soil analysis. You will then receive an evaluation and fertilizer information.
Tips
If the algae outgrowth in the aquarium or garden pond is too high, an excessively high phosphorus content could be to blame. You can easily determine this with a commercially available phosphate water test. A so-called “PhosphateMinus” product provides a remedy for the presence of phosphate contamination.








